Phenol
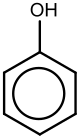
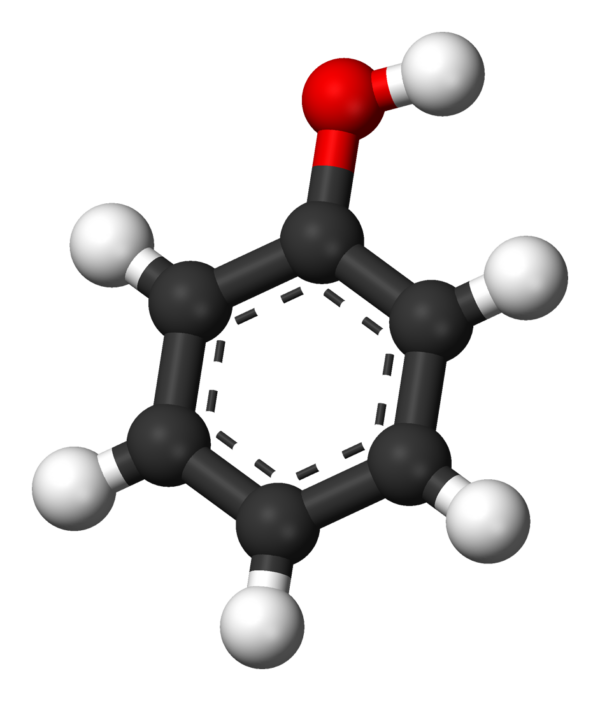
Phenol, or Benzenol, (also known as carbolic acid or phenolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group (−C6H5) bonded to a hydroxy group (−OH). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns.
Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 million tonnes a year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs.
Application
Phenol is used in the preparation of resins, dyes, explosives, lubricants, pesticides and plastics
| Chemical formula | C6H6O |
|---|---|
| Molar mass | 94.113 g/mol |
| Appearance | Transparent crystalline solid |
| Odor | Sweet and tarry |
| Density | 1.07 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 40.5 °C (104.9 °F; 313.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 181.7 °C (359.1 °F; 454.8 K) |
| Sloubility in water | 8.3 g/100 mL (20 °C) |
| Log P | 1.48 |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.4 mmHg (20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.95 (in water), |
| Conjugate base | Phenoxide |
| UV-vis (λmax) | 270.75nm |
| Dipole moment | 1.224 D |


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.