
Mono Ethylene Glycol
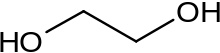
Ethylene glycol (IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal dio) with the formula (CH2OH)2. It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odorless, colorless, flammable, viscous liquid. Ethylene glycol has a sweet taste, but it is toxic in high concentrations. This molecule has been observed in outer space.
A higher selectivity is achieved by the use of Shell’s OMEGA process. In the OMEGA process, the ethylene oxide is first converted with carbon dioxide (CO2) to ethylene carbonate. This ring is then hydrolyzed with a base catalyst in a second step to produce mono-ethylene glycol in 98% selectivity. The carbon dioxide is released in this step again and can be fed back into the process circuit.
Application
It is primarily used as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and fabric industry, and used in bottling. A small percent is also used in industrial applications like antifreeze formulations and other industrial products.Used as raw material for polyester fibre, antifreezer, and as solvent in paint, ink, explosive, adhesive etc
| Chemical formula | C2H6O2 |
|---|---|
| Molar mass | 62.068 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.1132 g/cm3 (0.04022 lb/cu in) |
| Melting point | −12.9 °C (8.8 °F; 260.2 K) |
| Boiling point | 197.3 °C (387.1 °F; 470.4 K) |
| Solubility in water | Miscible |
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohols, ethyl acetate, THF, and dioxane. Miscible with DCM and slightly miscible with diethyl ether. Not miscible with toluene or hexanes. |
| log P | -1.69[ |
| Vapor pressure | 0.06 mmHg (20 °C)[ |
| Viscosity | 1.61×10−2 Pa·s |

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.