Formic Acid
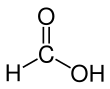
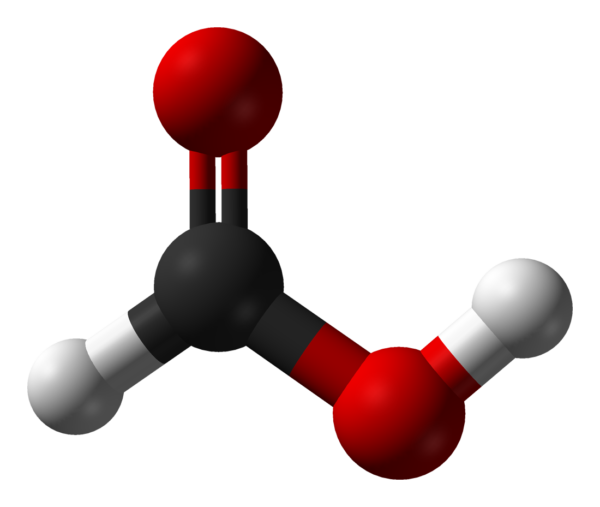
Formic acid (from Latin formica ‘ant’), systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid, and has the chemical formula HCOOH and structure H−C(=O)−O−H. It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some ants. Esters, salts and the anion derived from formic acid are called formates. Industrially, formic acid is produced from methanol.
Application
Formic acid is very frequently used in food products as a preservative or on crops as a pesticide. It is in the production of leather, textiles and leather.
| Chemical formula | CH2O2 |
|---|---|
| Molar mass | 46.025 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless fuming liquid |
| odor | Pungent, penetrating |
| Density | 1.220 g/mL |
| Melting Point | 8.4 °C (47.1 °F; 281.5 K) |
| Boiling Point | 100.8 °C (213.4 °F; 373.9 K) |
| Solubility in water | Miscible |
| Solubility | Miscible with ether, acetone, ethyl acetate, glycerol, methanol, ethanol |
| log P | -0.54 |
| Vapor pressure | 35 mmHg (20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.745 |
| Conjugate base | Formate |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −19.90×10−6 cm3/mol |



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.