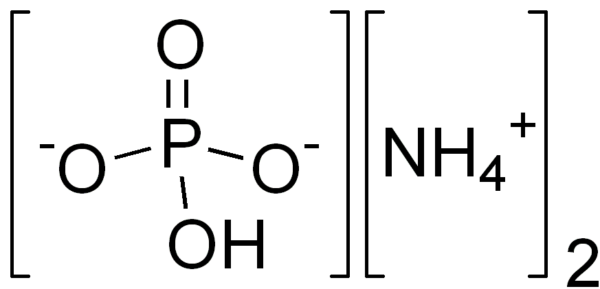
DAP (DIAMMONIUM PHOSPHATE)

Diammonium phosphate (DAP; IUPAC name diammonium hydrogen phosphate; chemical formula (NH4)2(HPO4) is one of a series of water-soluble ammonium phosphate salts that can be produced when ammonia reacts with phosphoric acid.
Solid diammonium phosphate shows a dissociation pressure of ammonia as given by the following expression and equation:
- (NH4)2HPO4(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + (NH4)H2PO4(s)
At 100 °C, the dissociation pressure of diammonium phosphate is approximately 5 mmHg.
According to the diammonium phosphate MSDS from CF Industries, Inc., decomposition starts as low as 70 °C: “Hazardous Decomposition Products: Gradually loses ammonia when exposed to air at room temperature. Decomposes to ammonia and monoammonium phosphate at around 70 °C (158 °F). At 155 °C (311 °F), DAP emits phosphorus oxides, nitrogen oxides and ammonia.
Application
Used to clarify the cane juice and to make sugar with better lustre and quality. In Food and beverages, used as acidifying agent and as tart flavouring agent in beverages such as various colas. It is used in the manufacture of industrial cleaning products, other inorganic and organic phosphoric chemicals, foundry resins, paints, enamels and refractory, antifreeze productions, and textile process materials. It is used in water treatment. Food grade phosphoric acid is used; as a acidulation in soft drink (particularly cola).
| Chemical formula | (NH4)2HPO4 |
|---|---|
| Molar mass | 132.06 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless monoclinic crystals |
| Density | 1.619 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 155 °C (311 °F; 428 K) decomposes |
| Solubility in water | 57.5 g/100 mL (10 °C) |
| Solubility | insoluble in alcohol, acetone and liquid ammonia |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.52 |



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.